Earth and Space Science (Grades 9–12)
Subtest 1 Sample Items
Recommendation for individuals using a screenreader: please set your punctuation settings to "most."
Expand All | Collapse All
Question 1
1. A researcher hypothesizes that the sunspot cycle has a significant effect on Earth's climate system. Which of the following types of data would verify this hypothesis?
- historical records that demonstrate cold conditions existed during the longest recorded solar minima
- results from computer modeling experiments that accurately recreate past climate conditions based on changes in solar activity
- the absence of a better explanation for observed changes in ocean surface temperatures during past solar cycles
- a mechanism that physically connects variations in solar output during the solar cycle to specific changes in the climate system
Answer to question 1
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: D. (Objective 0001) Although historical events, computer models, and the absence of contradictory data may all support the hypothesis, only a mechanism that definitively shows how variations in the solar cycle affect Earth's climate system would provide verification of the hypothesis.
Correct Response: D. (Objective 0001) Although historical events, computer models, and the absence of contradictory data may all support the hypothesis, only a mechanism that definitively shows how variations in the solar cycle affect Earth's climate system would provide verification of the hypothesis.
Question 2
2. Following the melting of the Pleistocene continental glaciers, Earth's lithosphere moved upward in response to the removal of the mass of ice. Which of the following unifying themes in the sciences best describes this isostatic rebound of the lithosphere?
- entropy
- equilibrium
- positive feedback
- conservation of mass
Answer to question 2
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: B. (Objective 0001) Isostacy is a mechanism that restores gravitational equilibrium to Earth's crust. Earth's gravity is a downward force acting on the crust due to the mass of the crust and the mass of overlying materials that rest on the crust, such as continental glaciers. When continental glaciers receded from much of the Northern Hemisphere, isostatic rebound worked to restore the gravitational equilibrium between the weight of Earth's lithosphere and the underlying asthenosphere. Isostacy is basically a specialized type of buoyancy in which the asthenosphere exerts an upward force on the overlying crust similar to water exerting an upward force on a cork that has been pushed down into the fluid. Similarly, lithosphere that has been pushed downward into the asthenosphere by a large mass of continental ice sheet moves upward once the overlying mass is removed.
Correct Response: B. (Objective 0001) Isostacy is a mechanism that restores gravitational equilibrium to Earth's crust. Earth's gravity is a downward force acting on the crust due to the mass of the crust and the mass of overlying materials that rest on the crust, such as continental glaciers. When continental glaciers receded from much of the Northern Hemisphere, isostatic rebound worked to restore the gravitational equilibrium between the weight of Earth's lithosphere and the underlying asthenosphere. Isostacy is basically a specialized type of buoyancy in which the asthenosphere exerts an upward force on the overlying crust similar to water exerting an upward force on a cork that has been pushed down into the fluid. Similarly, lithosphere that has been pushed downward into the asthenosphere by a large mass of continental ice sheet moves upward once the overlying mass is removed.
Question 3
3. Which of the following remote sensing technologies has been most often used for determining the depth and location of undersea oil deposits?
- ground-penetrating radar
- magnetometry
- seismic reflection and refraction
- sonar
Answer to question 3
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: C. (Objective 0001) Seismic reflection has been widely used by the oil industry to locate oil deposits in geologic deposits below the seafloor. In carrying out seismic reflection surveys, geophysicists produce a strong pulse of sound energy, using either an explosion or specialized tool to generate the sound energy. The differential reflection and refraction of these generated seismic waves can be interpreted to determine the depth and location of geologic structures, interfaces, and deposits of hydrocarbons.
Correct Response: C. (Objective 0001) Seismic reflection has been widely used by the oil industry to locate oil deposits in geologic deposits below the seafloor. In carrying out seismic reflection surveys, geophysicists produce a strong pulse of sound energy, using either an explosion or specialized tool to generate the sound energy. The differential reflection and refraction of these generated seismic waves can be interpreted to determine the depth and location of geologic structures, interfaces, and deposits of hydrocarbons.
Question 4
4. Which of the following procedures would be most effective for determining if a field sample of rock is limestone?
- placing several drops of dilute hydrochloric acid on a freshly exposed surface of the rock to see if the rock reacts with the acid
- rubbing a freshly exposed surface of the rock against a streak plate to determine the color of the streak produced on the plate
- heating the rock at a high temperature for at least half an hour to determine if carbon dioxide is released from the rock
- rubbing a solid piece of the rock against a standard set of minerals in the Mohs hardness scale to determine the rock's hardness
Answer to question 4
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: A. (Objective 0001) Limestone is composed almost entirely of calcium carbonate, a mineral that reacts chemically with dilute hydrochloric acid to produce water and carbon dioxide. The reaction can be observed as bubbling on the surface of the rock. This provides an effective method to determine whether or not a particular rock is limestone.
Correct Response: A. (Objective 0001) Limestone is composed almost entirely of calcium carbonate, a mineral that reacts chemically with dilute hydrochloric acid to produce water and carbon dioxide. The reaction can be observed as bubbling on the surface of the rock. This provides an effective method to determine whether or not a particular rock is limestone.
Question 5
5. Which of the following types of visual representations would be best suited for displaying information about the percent composition of minerals in a given sample of rock?
- histogram
- line graph
- tree diagram
- circle graph
Answer to question 5
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: D. (Objective 0001) A circle graph displays the parts of a whole, in their individual proportions. For example, a circle graph could help a reader quickly see how much of an igneous rock sample is feldspar, quartz, etc.
Correct Response: D. (Objective 0001) A circle graph displays the parts of a whole, in their individual proportions. For example, a circle graph could help a reader quickly see how much of an igneous rock sample is feldspar, quartz, etc.
Question 6
6. Multiple Global Positioning System (GPS) sensors continuously monitor the Yellowstone region of Wyoming. These sensors are primarily assessing which of the following variables related to the status of the underlying magma chamber of the Yellowstone supervolcano?
- ground deformation of the area
- strain in the faults underlying the caldera
- surface temperatures of the soil
- escape of gases into the atmosphere
Answer to question 6
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: A. (Objective 0001) Movements of magma can create changes on Earth's surface. Therefore, monitoring ground deformation can help predict volcanic eruption. GPS satellites can identify the location of a receiver through signals that emit information. By placing several GPS receivers on volcanoes and continuously collecting information about their locations, it is possible to detect whether the receivers' positions have shifted. Such a shift would indicate increasing volcanic activity below the surface.
Correct Response: A. (Objective 0001) Movements of magma can create changes on Earth's surface. Therefore, monitoring ground deformation can help predict volcanic eruption. GPS satellites can identify the location of a receiver through signals that emit information. By placing several GPS receivers on volcanoes and continuously collecting information about their locations, it is possible to detect whether the receivers' positions have shifted. Such a shift would indicate increasing volcanic activity below the surface.
Question 7
7. A hydrologist is developing a computer model of a drainage basin to determine the likelihood of flooding in different parts of the basin under various conditions. In developing the model, which of the following should the hydrologist do first?
- Develop an algorithm to represent frictional drag created between the river channels in the drainage basin and flood-stage streamflow.
- Establish the limitations of the computer model for predicting actual flood events along specific rivers in the drainage basin.
- Identify the variables and physical parameters that will have a significant effect on flooding in different parts of the drainage basin.
- Determine the type of computer hardware needed to run a large model with multiple variables that change over time.
Answer to question 7
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: C. (Objective 0002) A drainage basin is the land area that supplies all the runoff water that forms a river system. Development of a computer model that can be used to determine the likelihood of flooding in a drainage basin needs to take into account the climate conditions that affect the landscape (e.g., precipitation, temperature, wind speed). Additionally, the hydrology of the basin must be considered with regard to such things as runoff, water tables, and the moisture content of the soil. Finally, it is necessary to determine characteristics related to the physical structure of the basin itself, such as those characteristics related to topography, soil structure, and land cover.
Correct Response: C. (Objective 0002) A drainage basin is the land area that supplies all the runoff water that forms a river system. Development of a computer model that can be used to determine the likelihood of flooding in a drainage basin needs to take into account the climate conditions that affect the landscape (e.g., precipitation, temperature, wind speed). Additionally, the hydrology of the basin must be considered with regard to such things as runoff, water tables, and the moisture content of the soil. Finally, it is necessary to determine characteristics related to the physical structure of the basin itself, such as those characteristics related to topography, soil structure, and land cover.
Question 8
8. A background in which of the following disciplines within Earth and space science would be most useful for an individual interested in becoming an environmental engineer involved in the analysis and remediation of water pollution?
- meteorology
- geophysics
- mineralogy
- geochemistry
Answer to question 8
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: D. (Objective 0002) The analysis and remediation of water pollution typically involves collecting and analyzing water samples from freshwater bodies and groundwater aquifers and analyzing the geologic and hydrologic variables that may affect the location, concentration, and movement of contaminants in water. Geochemistry directly supports this work because it deals with the chemical reactions and processes that involve rock, water, and soils, as well as the cycling and transport of Earth's chemical components and their interactions with the hydrosphere and atmosphere.
Correct Response: D. (Objective 0002) The analysis and remediation of water pollution typically involves collecting and analyzing water samples from freshwater bodies and groundwater aquifers and analyzing the geologic and hydrologic variables that may affect the location, concentration, and movement of contaminants in water. Geochemistry directly supports this work because it deals with the chemical reactions and processes that involve rock, water, and soils, as well as the cycling and transport of Earth's chemical components and their interactions with the hydrosphere and atmosphere.
Question 9
9. The radioisotope carbon-14 is used for estimating the age of carbon-bearing materials that are up to 50,000 years old. Carbon-14 has a half-life of 5,730 years. A prehistoric piece of wood is determined to contain 3.125% of the original carbon-14 atoms that were in the wood when the tree it came from was cut down. Given the percentage of carbon-14 remaining in the piece of wood, what is the approximate age of the wood?
- 10,740 years old
- 22,920 years old
- 28,650 years old
- 34,380 years old
Answer to question 9
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: C. (Objective 0002) Radioactive decay is a statistical process that is described by an exponential function. The half-life of carbon-14 is 5,730 years. This means that after 5,730 years half of a given mass, M, of carbon-14 will remain,
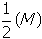 . After another 5,730 years
. After another 5,730 years
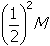 of the carbon-14 remains in the piece of wood, or
of the carbon-14 remains in the piece of wood, or
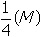 . If 3.125% of the original carbon-14 remains, this is equal to
. If 3.125% of the original carbon-14 remains, this is equal to
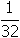 of the original mass of carbon-14. Since
of the original mass of carbon-14. Since
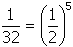 , the carbon-14 has decayed for 5 half-lives or 28,650 years.
Correct Response: C. (Objective 0002) Radioactive decay is a statistical process that is described by an exponential function. The half-life of carbon-14 is 5,730 years. This means that after 5,730 years half of a given mass, M, of carbon-14 will remain, One half open parenthesis M close parenthesis . After another 5,730 years Open parenthesis one half closed parenthesis squared M of the carbon-14 remains in the piece of wood, or One quarter open parethensis M closed parenthesis. If 3.125 percent of the original carbon-14 remains, this is equal to One over thirty-two of the original mass of carbon-14. Since One over thirty-two equals open parenthesis one half closed parenthesis sup five, the carbon-14 has decayed for 5 half-lives or 28,650 years.
, the carbon-14 has decayed for 5 half-lives or 28,650 years.
Correct Response: C. (Objective 0002) Radioactive decay is a statistical process that is described by an exponential function. The half-life of carbon-14 is 5,730 years. This means that after 5,730 years half of a given mass, M, of carbon-14 will remain, One half open parenthesis M close parenthesis . After another 5,730 years Open parenthesis one half closed parenthesis squared M of the carbon-14 remains in the piece of wood, or One quarter open parethensis M closed parenthesis. If 3.125 percent of the original carbon-14 remains, this is equal to One over thirty-two of the original mass of carbon-14. Since One over thirty-two equals open parenthesis one half closed parenthesis sup five, the carbon-14 has decayed for 5 half-lives or 28,650 years.
Question 10
10. For which of the following purposes would the celestial sphere model be most useful?
- analyzing the apparent motion of the planets as seen from Earth
- determining the distance of stars beyond the Milky Way galaxy
- predicting the evolution of planetary orbits based on gravitational forces
- evaluating the energy released by the sun at different stages in the solar cycle
Answer to question 10
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: A. (Objective 0002) The celestial sphere has no physical reality, but serves as a model for interpreting the motions and locations of stars and planets as seen from Earth. This Earth-centered model can be thought of as a concentric sphere surrounding Earth upon which all the objects visible from Earth are projected. Historically, it was a valuable tool in navigation and still provides a useful model for thinking about and analyzing the apparent motion of objects in the heavens.
Correct Response: A. (Objective 0002) The celestial sphere has no physical reality, but serves as a model for interpreting the motions and locations of stars and planets as seen from Earth. This Earth-centered model can be thought of as a concentric sphere surrounding Earth upon which all the objects visible from Earth are projected. Historically, it was a valuable tool in navigation and still provides a useful model for thinking about and analyzing the apparent motion of objects in the heavens.
Question 11
11. The geologic cross section below represents a glaciated landscape in the northernmost United States.
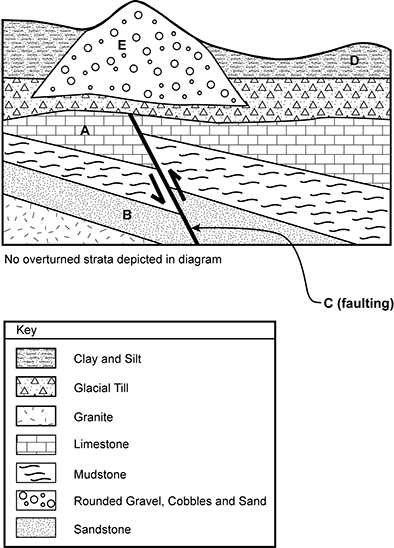
Layer D is clay and silt on the surface, layer e is rounded gravel, cobbles, and sand that begins in a layer of glacial till below layer D and extends upward through it. Layer A is limestone that resides under layers E and D. Layer B is sandstone and underlies layer A. A vertical offset fault labeled C runs through layers A and B. No overturned strata are depicted in the diagram.
Which of the following sequences of letters correctly orders the geologic events and strata from the oldest to the most recent?
- B, C, A, E, D
- E, D, C, A, B
- B, A, C, E, D
- C, B, A, D, E
Answer to question 11
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: C. (Objective 0002) Of the geologic deposits that are marked with letters, the oldest is the sandstone layer (B) that sits on top of the granite. The limestone layer (A) is younger than the sandstone layer as it is higher up in the stratigraphic sequence. Thrust faulting (C) was the next geologic event as it offset the layers of sedimentary rock that had already been deposited. The sedimentary deposits overlying the limestone were all deposited after the faulting occurred because the fault does not cross these deposits. The next major event was glaciation. While glacial till was being deposited, an esker (E) formed as sediment was deposited by an englacial or subglacial stream. Finally, clay and silt (D) were deposited, possibly in a glacial lake that formed in front of the receding glacier.
Correct Response: C. (Objective 0002) Of the geologic deposits that are marked with letters, the oldest is the sandstone layer (B) that sits on top of the granite. The limestone layer (A) is younger than the sandstone layer as it is higher up in the stratigraphic sequence. Thrust faulting (C) was the next geologic event as it offset the layers of sedimentary rock that had already been deposited. The sedimentary deposits overlying the limestone were all deposited after the faulting occurred because the fault does not cross these deposits. The next major event was glaciation. While glacial till was being deposited, an esker (E) formed as sediment was deposited by an englacial or subglacial stream. Finally, clay and silt (D) were deposited, possibly in a glacial lake that formed in front of the receding glacier.
Question 12
12. An Earth and space science teacher uses both verbal explanations and nonverbal representations (e.g., relevant diagrams, graphic organizers) to introduce students to new content-specific vocabulary from an academic article they will be reading. Which of the following student activities would be most effective in supporting the students' comprehension of the article by reinforcing their understanding of the new vocabulary?
- defining the new vocabulary in their own words
- developing a word search using the new vocabulary
- underlining the new vocabulary as they read the article
- writing the new vocabulary in their content notebooks
Answer to question 12
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: A. (Objective 0003) Restating a definition in one's own words, or paraphrasing, requires students to reflect on the meaning of the word and use synonyms and/or explanations for key concepts that differ from those used in the definition, while still conveying the same idea. To accomplish this successfully, students need to think about the meaning of the word at a fairly deep level, which enhances both understanding and retention of the new vocabulary word.
Correct Response: A. (Objective 0003) Restating a definition in one's own words, or paraphrasing, requires students to reflect on the meaning of the word and use synonyms and/or explanations for key concepts that differ from those used in the definition, while still conveying the same idea. To accomplish this successfully, students need to think about the meaning of the word at a fairly deep level, which enhances both understanding and retention of the new vocabulary word.
Question 13
13. A science teacher regularly preteaches key vocabulary words from a text before having students read the text independently. As part of this instruction, the teacher writes several sentences from the text on the board, highlighting the target words' spelling and relevant morphological features (e.g., affixes, roots). Which of the following rationales best explains why this practice would be effective in promoting students' ability to read and comprehend the text?
- A word may have both a general meaning and a content-specific meaning, and students need to be able to determine which meaning is relevant in a particular context.
- Accurate, rapid word identification allows students to focus their attention during reading on learning the text's content rather than on trying to decode individual words.
- Social and academic language often differ, so students need to recognize similarities and differences between language structures used in spoken and written language.
- The ability to use cognitive and metacognitive reading strategies is enhanced when students are also taught when and how to use the strategies in the context of authentic texts.
Answer to question 13
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: B. (Objective 0003) The instruction described promotes development of accurate, rapid identification of the target words during reading by integrating instruction in the meaning of the words with explicit instruction and practice in recognizing the written form of the words. Careful attention to the spelling of the words and the morphological "chunks" within words promotes accurate decoding, and repeated exposure to the written word in a meaningful context builds automatic word recognition during reading. Convergent research indicates that automaticity is essential to reading fluency and comprehension.
Correct Response: B. (Objective 0003) The instruction described promotes development of accurate, rapid identification of the target words during reading by integrating instruction in the meaning of the words with explicit instruction and practice in recognizing the written form of the words. Careful attention to the spelling of the words and the morphological "chunks" within words promotes accurate decoding, and repeated exposure to the written word in a meaningful context builds automatic word recognition during reading. Convergent research indicates that automaticity is essential to reading fluency and comprehension.
14. Use the passage below to answer the question that follows.
Several students in an Earth and space science class are English language learners who have advanced-level (i.e., Level 5—bridging level) English language proficiency and demonstrate good foundational reading skills and subject-matter knowledge. The teacher will be assigning the class to read a new Earth and space science text.
Question 14
Given this scenario, which of the following strategies would be most appropriate for the teacher to use to differentiate the lesson for the English language learners in the class?
- arranging for the English language learners to read a translation of the text or a similar text written in their primary language
- providing the English language learners with a text about similar content that was written in English for students at a lower grade level
- explicitly preteaching the English language learners any idiomatic expressions and vocabulary essential for comprehending the text in English
- teaching the content of the text to the English language learners using an oral-presentation format rather than requiring them to read the assigned text
Answer to question14
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: C. (Objective 0003) The English language learners in this scenario are at the advanced level (i.e., Level 5—bridging level) of English language proficiency and have good literacy skills and content knowledge. English language learners with this background should be able to read grade-level texts in English with support, including comprehending the texts at the literal and inferential levels. The teacher may need to introduce new academic language to all the students prior to assigning the text. However, unlike their peers who are proficient in English or who were raised in homes where English is the primary language, the English language learners are also likely to be unfamiliar with idiomatic expressions and everyday vocabulary used in the text that are essential for comprehension. Thus, preteaching such words and expressions is an appropriate way to differentiate the lesson for advanced-level English language learners.
Correct Response: C. (Objective 0003) The English language learners in this scenario are at the advanced level (i.e., Level 5—bridging level) of English language proficiency and have good literacy skills and content knowledge. English language learners with this background should be able to read grade-level texts in English with support, including comprehending the texts at the literal and inferential levels. The teacher may need to introduce new academic language to all the students prior to assigning the text. However, unlike their peers who are proficient in English or who were raised in homes where English is the primary language, the English language learners are also likely to be unfamiliar with idiomatic expressions and everyday vocabulary used in the text that are essential for comprehension. Thus, preteaching such words and expressions is an appropriate way to differentiate the lesson for advanced-level English language learners.
Question 15
15. Helping students learn how to reflect on, monitor, and regulate their own thinking processes supports their content-area reading primarily by improving their ability to:
- read content-area texts accurately and at an appropriate rate.
- apply comprehension strategies when reading content-area texts.
- deconstruct the syntax of complex sentences found in content-area texts.
- determine the meaning of unfamiliar multisyllabic words in content-area texts.
Answer to question 15
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response:B. (Objective 0003) There are a variety of comprehension strategies that can be used before, during, and/or after reading. For students to be able to select and adapt the right strategy for a particular text or reading situation, they need to use metacognitive knowledge and metacognitive control; that is, they need to be aware of how they are thinking and learning as they read and be able to adapt their learning approaches as necessary.
Correct Response: B. (Objective 0003) There are a variety of comprehension strategies that can be used before, during, and/or after reading. For students to be able to select and adapt the right strategy for a particular text or reading situation, they need to use metacognitive knowledge and metacognitive control; that is, they need to be aware of how they are thinking and learning as they read and be able to adapt their learning approaches as necessary.
Question 16
16. Copper's high electrical conductivity is primarily due to which of the following?
- the electronegativity of copper atoms
- the existence of a charge imbalance in copper atoms
- the density of copper atoms in a crystal lattice
- the presence of delocalized valence electrons in copper atoms
Answer to question 16
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: C. (Objective 0004) Each copper atom has a single valence electron in its outer shell. This electron is able to move freely among the positive copper ions within the crystal lattice structure. This ability for free movement of a copper atom's valence electron contributes to the high electrical conductivity of copper wire. When a copper wire is attached to a battery, the electrons will flow inside the wire, creating an electric current.
Correct Response: C. (Objective 0004) Each copper atom has a single valence electron in its outer shell. This electron is able to move freely among the positive copper ions within the crystal lattice structure. This ability for free movement of a copper atom's valence electron contributes to the high electrical conductivity of copper wire. When a copper wire is attached to a battery, the electrons will flow inside the wire, creating an electric current.
Question 17
17. Large bodies of water play an important role in moderating temperature extremes on Earth. This characteristic of water is most directly related to the:
- hydrogen bonds between water molecules that cause water to have a high specific heat capacity.
- dense packing of water molecules that increases the energy needed to increase the kinetic energy of water.
- covalent bonds between the atoms in water that increase the energy required to evaporate water.
- slow rate at which water molecules break into their constituent hydrogen and oxygen atoms when heated.
Answer to question 17
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: A. (Objective 0004) Each oxygen atom in a water molecule has two hydrogen bonds connecting it to another water molecule. The hydrogen atoms in that same water molecule are also connected to the oxygen atom of another water molecule, producing a three-dimensional structure in which each water molecule is tetrahedrally bonded to four hydrogen atoms. This structural network gives water many of its unique properties, including its high specific heat capacity.
Correct Response: A. (Objective 0004) Each oxygen atom in a water molecule has two hydrogen bonds connecting it to another water molecule. The hydrogen atoms in that same water molecule are also connected to the oxygen atom of another water molecule, producing a three-dimensional structure in which each water molecule is tetrahedrally bonded to four hydrogen atoms. This structural network gives water many of its unique properties, including its high specific heat capacity.
Question 18
18. Which of the following minerals has a very high specific gravity and a metallic luster, and is a potentially hazardous substance that is also a commercially important ore?
- halite (NaCl)
- pyrite (FeS2)
- galena (PbS)
- graphite (C)
Answer to question 18
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: C. (Objective 0004) Galena (lead sulfide) has a very high specific gravity (7.4–7.6) and a metallic luster, and is an important ore from which lead is obtained. Although lead sulfide is generally insoluble, and therefore not highly toxic, extensive exposure to lead sulfide during processing and mining can be hazardous due to possible exposure to elemental lead.
Correct Response: C. (Objective 0004) Galena (lead sulfide) has a very high specific gravity (7.4–7.6) and a metallic luster, and is an important ore from which lead is obtained. Although lead sulfide is generally insoluble, and therefore not highly toxic, extensive exposure to lead sulfide during processing and mining can be hazardous due to possible exposure to elemental lead.
Question 19
19. The formation of the East African Rift Valley is associated with the development of which of the following large-scale geologic structures?
- thrust fault
- convergent plate boundary
- subduction zone
- horst and graben
Answer to question 19
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: D. (Objective 0004) The East African Rift Valley is an example of a continental tectonic plate that is being pulled apart by extensional forces. As these extensional forces pull the crust apart, the crust is fractured, producing numerous normal faults. Some sections of the crust, called grabens, drop down while other sections, called horsts, move upward along the faults. These horst and graben geologic structures are associated with rift valleys in many parts of the world, commonly forming fault-block mountain ranges with steep escarpments and adjacent sediment-filled valleys.
Correct Response: D. (Objective 0004) The East African Rift Valley is an example of a continental tectonic plate that is being pulled apart by extensional forces. As these extensional forces pull the crust apart, the crust is fractured, producing numerous normal faults. Some sections of the crust, called grabens, drop down while other sections, called horsts, move upward along the faults. These horst and graben geologic structures are associated with rift valleys in many parts of the world, commonly forming fault-block mountain ranges with steep escarpments and adjacent sediment-filled valleys.
Question 20
20. The monsoon wind system of India brings abundant summer rainfall to parts of India that are typically dry during the winter months. The summer monsoon that brings the rain is driven by which of the following factors?
- a southward shift in the location of the subtropical jet stream
- increased contrast between the temperature of the land surface and the cooler ocean
- a northward shift in the position of the intertropical convergence zone
- increased evaporation from the ocean as the temperature of ocean surface water rises
Answer to question 20
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: B. (Objective 0004) India's summer monsoon is somewhat like a large-scale sea breeze. In summer, the air over the continental interior becomes much warmer than the air overlying the water as water is slow to warm while the continental interior heats up relatively rapidly. As the air over the continental interior warms, a shallow thermal low-pressure system develops. The heated air within the low-pressure system rises, pulling the surrounding air into the low in a counterclockwise flow. This circulation pattern pulls very moist air from the oceans into the interior of the continent. The moist air rises as it is pulled into the area of low pressure and as it is forced upward by mountains. This causes the water vapor in the air to cool to the saturation point, producing heavy rain and thunderstorms.
Correct Response: B. (Objective 0004) India's summer monsoon is somewhat like a large-scale sea breeze. In summer, the air over the continental interior becomes much warmer than the air overlying the water as water is slow to warm while the continental interior heats up relatively rapidly. As the air over the continental interior warms, a shallow thermal low-pressure system develops. The heated air within the low-pressure system rises, pulling the surrounding air into the low in a counterclockwise flow. This circulation pattern pulls very moist air from the oceans into the interior of the continent. The moist air rises as it is pulled into the area of low pressure and as it is forced upward by mountains. This causes the water vapor in the air to cool to the saturation point, producing heavy rain and thunderstorms.
Question 21
21. Earth's magnetic field is thought to be generated primarily by which of the following actions?
- convection currents carrying heat produced in the core through the mantle
- friction between the inner and outer cores due to differing speeds of rotation
- circulation of metallic fluids caused by heat transfer in the molten outer core
- large depositions of magnetite and other metallic minerals under the polar regions
Answer to question 21
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: C. (Objective 0004) The hottest, densest part of Earth is in its inner core, composed of solid metals—primarily iron. The next layer, the outer core, is under less pressure, and metals such as iron and nickel are in the liquid state. Convection currents occur here so that as hotter matter rises, cooler and denser matter falls. Electrons from this flow of metal create electric currents, and these currents create magnetic fields. Caused by the rotation of Earth, the Coriolis effect curves the flow of current such that the many magnetic fields align, creating Earth's magnetic field.
Correct Response: C. (Objective 0004) The hottest, densest part of Earth is in its inner core, composed of solid metals—primarily iron. The next layer, the outer core, is under less pressure, and metals such as iron and nickel are in the liquid state. Convection currents occur here so that as hotter matter rises, cooler and denser matter falls. Electrons from this flow of metal create electric currents, and these currents create magnetic fields. Caused by the rotation of Earth, the Coriolis effect curves the flow of current such that the many magnetic fields align, creating Earth's magnetic field.
Question 22
22. In which of the following scenarios would the atmosphere be most unstable and therefore most likely to produce severe thunderstorms?
- Upper levels of the atmosphere are significantly cooler than lower levels, supporting convection of warm, moist air.
- High pressure dominates in the upper levels of the atmosphere, causing rapid condensation of rising water vapor.
- Moist air in the upper troposphere sinks rapidly into a dry air mass below, causing downdrafts and straight-line winds.
- Jet stream winds are absent, supporting steady localized convection of warm air into the midlevels of the atmosphere.
Answer to question 22
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: A. (Objective 0005) Instability in the atmosphere is an essential ingredient of severe weather. The atmosphere is said to be conditionally unstable when the drop in temperature with increasing elevation is sufficient to support the upward movement of a warm, saturated air mass due to the buoyant force acting on the air mass. This occurs because a moist air mass is less dense than a dry air mass and a warm air mass is less dense than a cool air mass. In addition, as a warm, moist air mass rises into cooler air higher up in the atmosphere, the condensation that occurs releases additional heat into the rising air mass, allowing it to continue to rise. Ultimately, the convection of this warm, moist air into cooler air aloft supports the formation of severe thunderstorms.
Correct Response: A. (Objective 0005) Instability in the atmosphere is an essential ingredient of severe weather. The atmosphere is said to be conditionally unstable when the drop in temperature with increasing elevation is sufficient to support the upward movement of a warm, saturated air mass due to the buoyant force acting on the air mass. This occurs because a moist air mass is less dense than a dry air mass and a warm air mass is less dense than a cool air mass. In addition, as a warm, moist air mass rises into cooler air higher up in the atmosphere, the condensation that occurs releases additional heat into the rising air mass, allowing it to continue to rise. Ultimately, the convection of this warm, moist air into cooler air aloft supports the formation of severe thunderstorms.
Question 23
23. During a particularly long and intense heat wave in Texas, meteorologists regularly referenced the ongoing drought in the state as a contributing factor involved in the record-breaking high temperatures. Which of the following explanations best describes the primary reason that drought conditions are believed to increase the air temperature during a heat wave?
- Formation of fog that typically accompanies daily changes in temperature in the South is absent, increasing nighttime temperatures.
- Evapotranspiration, which cools the air as water changes phase from a liquid to a gas, is reduced significantly during a drought.
- Mixing in the atmosphere is greatly reduced by the absence of cold or warm fronts moving through the region during a drought.
- High atmospheric pressure that typically dominates during a drought creates a thermal inversion that traps hot air at the surface.
Answer to question 23
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: B. (Objective 0005) Evapotranspiration is the loss of water by both evaporation from the soil and transpiration from the plants living in the soil. This process is an important cooling mechanism for the near-surface layer of the atmosphere. As water changes phase from liquid to gas, it absorbs energy from its surroundings. During a drought, the drop in evapotranspiration means less of the sun's energy is used to evaporate water and more of the sun's energy heats the ground surface. Increased warmth of the ground conducts more heat into the overlying air. This phenomenon contributes to the intensity of heat waves that occur during droughts.
Correct Response: B. (Objective 0005) Evapotranspiration is the loss of water by both evaporation from the soil and transpiration from the plants living in the soil. This process is an important cooling mechanism for the near-surface layer of the atmosphere. As water changes phase from liquid to gas, it absorbs energy from its surroundings. During a drought, the drop in evapotranspiration means less of the sun's energy is used to evaporate water and more of the sun's energy heats the ground surface. Increased warmth of the ground conducts more heat into the overlying air. This phenomenon contributes to the intensity of heat waves that occur during droughts.
Question 24
24. The development of which of the following conditions would most likely support the formation of a tornado as part of a supercell thunderstorm?
- flow of warm dry air up and over a moist cool air mass at the center of the
- high atmospheric pressure aloft that produces strong downdrafts within the storm center
- strong jet stream winds blowing in the same direction that the storm is moving
- vertical wind shear caused by surface winds blowing in a different direction than winds aloft
Answer to question 24
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: D. (Objective 0005) Although tornado formation is still not completely understood, tornadoes most often form in association with supercell thunderstorms when there is a significant change in the direction and speed of winds with elevation. If winds at the surface blow from the southeast, for example, while strong winds aloft are blowing from the west, the almost opposite direction of the two wind fields supports the formation of horizontal vortex tubes near the base of the supercell thunderstorm. Eventually, updrafts in the supercell thunderstorm carry the vortex tube into the heart of the thunderstorm, producing a rotating column of air that is now angled toward the vertical. This vertical rotating column of air can then form a funnel cloud that may or may not touch the ground surface as a potentially destructive tornado.
Correct Response: D. (Objective 0005) Although tornado formation is still not completely understood, tornadoes most often form in association with supercell thunderstorms when there is a significant change in the direction and speed of winds with elevation. If winds at the surface blow from the southeast, for example, while strong winds aloft are blowing from the west, the almost opposite direction of the two wind fields supports the formation of horizontal vortex tubes near the base of the supercell thunderstorm. Eventually, updrafts in the supercell thunderstorm carry the vortex tube into the heart of the thunderstorm, producing a rotating column of air that is now angled toward the vertical. This vertical rotating column of air can then form a funnel cloud that may or may not touch the ground surface as a potentially destructive tornado.
Question 25
25. The extent of future warming of Earth's climate is hard to predict because of the interplay of positive and negative feedback loops. In the context of a warming atmosphere, which of the following is the best example of a positive feedback loop in the atmosphere-hydrosphere system that would increase warming?
- Higher ocean temperatures increase the release of methane from the ocean floor, raising methane levels in the atmosphere.
- A rise in atmospheric temperatures increases evaporation rates from the ocean surface, generating more cloud cover.
- Increased carbon dioxide dissolved in the oceans damages coral reefs, reducing respiration and productivity of marine organisms.
- A longer melt season in the Arctic leads to greater absorption of solar energy, increasing carbon fixation by plankton.
Answer to question 25
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: A. (Objective 0005) As ocean temperatures increase, scientists believe that deposits of methane held in clathrate hydrates in sediments of the seafloor are going to become unstable, releasing the methane. As methane is an extremely effective greenhouse gas, it is believed that the release of methane from these deposits into the atmosphere would significantly increase the heat-trapping properties of the atmosphere. This is a classic positive feedback loop because the initial cause of the release of the methane from clathrate hydrates is warming of the ocean due to atmospheric warming.
Correct Response: A. (Objective 0005) As ocean temperatures increase, scientists believe that deposits of methane held in clathrate hydrates in sediments of the seafloor are going to become unstable, releasing the methane. As methane is an extremely effective greenhouse gas, it is believed that the release of methane from these deposits into the atmosphere would significantly increase the heat-trapping properties of the atmosphere. This is a classic positive feedback loop because the initial cause of the release of the methane from clathrate hydrates is warming of the ocean due to atmospheric warming.
Question 26
26. Which of the following processes is the most significant initial source of energy that contributes to hurricane formation?
- reflection of solar energy, radiating from the surface of the ocean and heating the layer of air just above it
- heating of portions of the ocean's surface, created by concentrated solar energy focusing the heat into large circular cells
- short-lived convective events, moving the solar energy stored in the oceanic surface water to cooler continental air masses
- storage of solar energy, obtained as ocean water evaporates and transforms from a liquid to a gaseous state
Answer to question 26
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: D. (Objective 0005) Latent heat is the energy needed to convert a more ordered state of matter to a less ordered one without a change in temperature. During the evaporation of water from the ocean's surface, energy (originally provided by sunlight) is added to the liquid water without raising its temperature until the liquid water is transformed into water vapor. The energy is retained in the water vapor and released when the vapor cools and condenses back into a liquid. It is this release of energy that drives the formation of hurricanes over tropical oceans.
Correct Response: D. (Objective 0005) Latent heat is the energy needed to convert a more ordered state of matter to a less ordered one without a change in temperature. During the evaporation of water from the ocean's surface, energy (originally provided by sunlight) is added to the liquid water without raising its temperature until the liquid water is transformed into water vapor. The energy is retained in the water vapor and released when the vapor cools and condenses back into a liquid. It is this release of energy that drives the formation of hurricanes over tropical oceans.
Question 27
27.
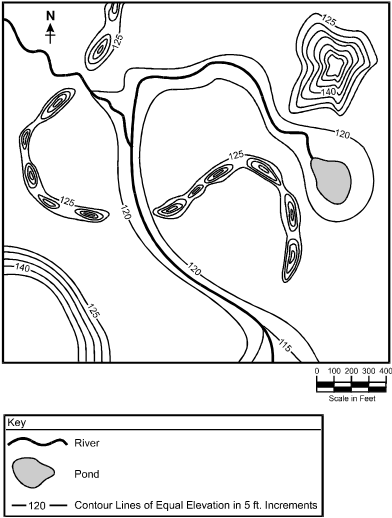
Topographic map depicting the elevations of landforms in a glaciated region of the northern United States. The geologic feature asked about in the question is depicted on the map as a winding series of three narrow hills that together form an "S" shape. This series of hills is not more than 100 feet wide in any section and the total length of the three hills together is approximately 3000 feet. There are two rivers that cut through the "S" shape, dividing it into the three separate hills. The elevation of this winding series of hills ranges from 125 feet to 140 feet, making the hills about 15 feet higher than the surrounding land surface, which has an elevation between 120 feet and 125 feet.
The topographic map shown above represents a glaciated region of the northern United States. The winding series of small hills that crosses the center of the map is composed of stratified coarse sand, gravel, and cobbles. Given its composition and shape, this series of hills is most likely which of the following types of glacial features?
- kame terrace
- esker
- terminal moraine
- drumlin
Answer to question 27
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: B. (Objective 0006). The long, narrow hills depicted in the map represent eskers. These structures are formed as a result of sand and gravel, as well as occasionally cobbles, that were deposited by streams of water flowing beneath a glacier. When the glacier melts, these depositional features remain and are often located near the terminus of the glacier.
Correct Response: B. (Objective 0006). The long, narrow hills depicted in the map represent eskers. These structures are formed as a result of sand and gravel, as well as occasionally cobbles, that were deposited by streams of water flowing beneath a glacier. When the glacier melts, these depositional features remain and are often located near the terminus of the glacier.
Question 28
28. A geologist investigating a sandstone outcrop hypothesizes that the sand grains that formed the sandstone were originally deposited in a sand dune. Which of the following types of data would be most helpful for the geologist to collect to support the hypothesis?
- the bedding characteristics of the outcrop and the sorting of sand grains
- the chemical composition of the sand grains and of the cementing agent that binds them together
- the absence of fossils of marine or freshwater organisms in the outcrop
- the thickness of the outcrop and the presence of unconformities above or below the sandstone strata
Answer to question 28
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: A. (Objective 0006) Since the sand grains in a sand dune are deposited be wind, they are typically well sorted. The nature of how dunes form and move often means the sand in a dune shows distinctive cross-bedding. This cross-bedding is preserved as the dune is lithified over time and becomes sandstone.
Correct Response: A. (Objective 0006) Since the sand grains in a sand dune are deposited be wind, they are typically well sorted. The nature of how dunes form and move often means the sand in a dune shows distinctive cross-bedding. This cross-bedding is preserved as the dune is lithified over time and becomes sandstone.
Question 29
29. Which of the following compounds plays a central role in the chemical weathering of limestone?
- humic acid
- hydroxyl ion
- carbonic acid
- acetate ion
Answer to question 29
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: C. (Objective 0006) When water combines with carbon dioxide, it generates carbonic acid. The carbonic acid reacts with carbonate rocks, such as limestone (calcium carbonate), to form the highly soluble calcium bicarbonate. This process is directly involved in the chemical weathering of limestone and the movement of carbon through the lithosphere, atmosphere, and hydrosphere as part of geochemical cycling of carbon.
Correct Response: C. (Objective 0006) When water combines with carbon dioxide, it generates carbonic acid. The carbonic acid reacts with carbonate rocks, such as limestone (calcium carbonate), to form the highly soluble calcium bicarbonate. This process is directly involved in the chemical weathering of limestone and the movement of carbon through the lithosphere, atmosphere, and hydrosphere as part of geochemical cycling of carbon.
Question 30
30. In which of the following geologic settings are precious metals, such as gold and silver, typically concentrated by geologic processes?
- the continental shelf where underwater landslides separate minerals by density
- the interface between the former land surface and a pyroclastic flow generated by a volcanic eruption
- the zone of transverse faulting between an oceanic plate and a continental plate
- the fractured contact zone between a cooling intrusive igneous body and the surrounding bedrock
Answer to question 30
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: D. (Objective 0006) As a large intrusive igneous body cools down, metal-rich fluids derived from the cooling magma are among the last components of the magma body to solidify from the parent igneous body. These hydrothermal fluids are forced into the fractured country rock surrounding a large igneous intrusive body, where they cool to form valuable ore deposits. Many of the world's most important deposits of gold, lead, zinc, and silver are generated from hydrothermal solutions that flowed away from cooling igneous bodies into the surrounding bedrock. The gold deposits in the foothills of California's Sierra Nevada Mountains are a classic example of the hydrothermal concentration of precious metals surrounding a large intruded igneous body.
Correct Response: D. (Objective 0006) As a large intrusive igneous body cools down, metal-rich fluids derived from the cooling magma are among the last components of the magma body to solidify from the parent igneous body. These hydrothermal fluids are forced into the fractured country rock surrounding a large igneous intrusive body, where they cool to form valuable ore deposits. Many of the world's most important deposits of gold, lead, zinc, and silver are generated from hydrothermal solutions that flowed away from cooling igneous bodies into the surrounding bedrock. The gold deposits in the foothills of California's Sierra Nevada Mountains are a classic example of the hydrothermal concentration of precious metals surrounding a large intruded igneous body.
Question 31
31. Drumlins are elongated glacial features that exist, often in large groups called drumlin fields, in many glaciated regions of the northern United States. Which of the following best describes how these elongated glacial deposits form?
- Ponds that form in front of stagnant glaciers fill with sediments that are exposed by erosion and shaped by wind into drumlins.
- Active glaciers and the running water at their base reshape previously deposited glacial sediments into drumlins as they flow over them.
- Sediments build up along the edges of valley glaciers and as the glaciers recede the sediments are shaped into drumlins by erosion.
- Water that pools on top of receding glaciers drains through cracks to the base of the ice, forming drumlin-shaped channels filled with sediments.
Answer to question 31
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: B. (Objective 0006) Drumlins are believed to form by the action of active glaciers on sediments underlying the glacier. Their elongated shape and sediments within drumlins indicate that the long axis of a drumlin is typically aligned with the flow direction of the glacier that formed it. They are composed of glacial till and often show separate layers of deposition, probably indicating the erosion, deposition, erosion, and redeposition of glacial sediments beneath a glacier.
Correct Response: B. (Objective 0006) Drumlins are believed to form by the action of active glaciers on sediments underlying the glacier. Their elongated shape and sediments within drumlins indicate that the long axis of a drumlin is typically aligned with the flow direction of the glacier that formed it. They are composed of glacial till and often show separate layers of deposition, probably indicating the erosion, deposition, erosion, and redeposition of glacial sediments beneath a glacier.
Question 32
32. Soil pH is one characteristic affected both by the material from which the soil developed and the conditions under which it developed. Which of the following geologic and climatological conditions would likely produce a soil with the highest acidity?
- weathering of a basalt sill in a semi-arid temperate climate with low rainfall
- weathering of limestone in a tropical climate with moderate seasonal rainfall
- weathering of marble in a Mediterranean climate with moderate rainfall
- weathering of a granite batholith in a subtropical climate with frequent rainfall
Answer to question 32
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: D. (Objective 0006) Weathering is the process by which rocks and their minerals are broken down into soil by physical, chemical, or biological means. Soil pH is determined by its concentration of hydrogen ions: the more hydrogen ions present, the lower the pH, and the higher the soil acidity. Granite is an acidic igneous rock, and frequent precipitation will remove soluble ions, increasing the concentration of hydrogen ions in the soil over time. Precipitation and percolating rainwater are typically mildly acidic because dissolved carbon dioxide in the water forms carbonic acid. Together, this means that with greater rainfall and more hydrogen ions present in a soil, a given soil will be more acidic.
Correct Response: D. (Objective 0006) Weathering is the process by which rocks and their minerals are broken down into soil by physical, chemical, or biological means. Soil pH is determined by its concentration of hydrogen ions: the more hydrogen ions present, the lower the pH, and the higher the soil acidity. Granite is an acidic igneous rock, and frequent precipitation will remove soluble ions, increasing the concentration of hydrogen ions in the soil over time. Precipitation and percolating rainwater are typically mildly acidic because dissolved carbon dioxide in the water forms carbonic acid. Together, this means that with greater rainfall and more hydrogen ions present in a soil, a given soil will be more acidic.
Question 33
33. Which of the following types of rock is most susceptible to chemical weathering?
- shale
- limestone
- mica
- sandstone
Answer to question 33
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: B. (Objective 0006) Rocks that contain large amounts of calcium carbonate, such as limestone, are particularly susceptible to chemical weathering since calcium carbonate reacts with water, especially if the water is somewhat acidic. For example, karst topography consists of chemically eroded limestone caves and demonstrates the ease with which limestone is chemically weathered.
Correct Response: B. (Objective 0006) Rocks that contain large amounts of calcium carbonate, such as limestone, are particularly susceptible to chemical weathering since calcium carbonate reacts with water, especially if the water is somewhat acidic. For example, karst topography consists of chemically eroded limestone caves and demonstrates the ease with which limestone is chemically weathered.
Question 34
34.
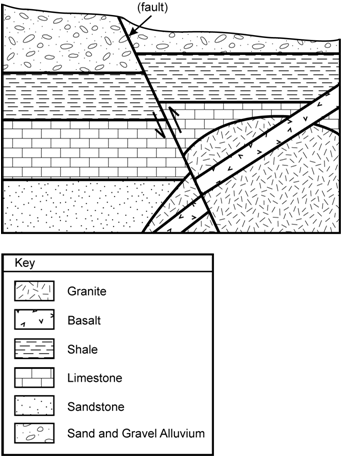
Geologic cross section depicting sedimentary deposits, a granitic intrusion, a basalt dike, and a fault. The fault bisects all geologic deposits in the cross section. The sequence of sediments from the top of the cross section to the bottom is as follows: Sand and gravel alluvium at the top, below that shale, below that limestone, and below that sandstone. Both the limestone and sandstone deposits are shown partially covered by a semicircular mass of granite (i.e., a granite batholith) in the lower right-hand corner of the cross section. A basalt dike crosses over the granite from the upper right-hand corner to the lower left. Just above the granite, in the upper right-hand corner of the cross section, the basalt dike also crosses over the shale layer and the limestone layer before continuing over the granite. The fault cuts through all the deposits, including the granite batholith and basalt dike and is located in the approximate middle of the cross section. The fault is tilted to the left about 30 degrees from the perpendicular. All geologic deposits on the right hand side of the fault have been pushed up relative to deposits to the left of the fault.
Ignoring the surface sand and gravel alluvium, which of the following correctly lists a possible sequence of the geologic events depicted in the cross section from the earliest event to the most recent?
- basalt dike intruded → sedimentary rocks deposited → granite batholith emplaced → faulting
- faulting → granite batholith emplaced → basalt dike intruded → sedimentary rocks deposited
- granite batholith emplaced → sedimentary rocks deposited → faulting → basalt dike intruded
- sedimentary rocks deposited → granite batholith emplaced → basalt dike intruded → faulting
- basalt dike intruded, sedimentary rocks deposited, granite batholith emplaced, faulting
- faulting, granite batholith emplaced, basalt dike intruded, sedimentary rocks deposited
- granite batholith emplaced, sedimentary rocks deposited, faulting, basalt dike intruded
- sedimentary rocks deposited, granite batholith emplaced, basalt dike intruded, faulting
Answer to question 34
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: D. (Objective 0007). Based on the law of superposition, in this cross section, the oldest geologic deposits are the sedimentary layers (the sandstone, limestone, and shale) and, thus, were deposited first. The granite batholith is younger than the surrounding sedimentary layers, according to the principle of cross-cutting relationships. Likewise, the occurrence of basalt dike intrusion occurred after the formation of the granite batholith. Finally, movement occurred along the indicated fault line as it cut across all geologic features. This is the most recent geological occurrence since it cut across all the rock layers.
Correct Response: D. (Objective 0007). Based on the law of superposition, in this cross section, the oldest geologic deposits are the sedimentary layers (the sandstone, limestone, and shale) and, thus, were deposited first. The granite batholith is younger than the surrounding sedimentary layers, according to the principle of cross-cutting relationships. Likewise, the occurrence of basalt dike intrusion occurred after the formation of the granite batholith. Finally, movement occurred along the indicated fault line as it cut across all geologic features. This is the most recent geological occurrence since it cut across all the rock layers.
Question 35
35. Researchers studying the transition between the Cretaceous and Tertiary periods discovered sedimentary layers that contain much more of the rare element iridium than is normally found in sedimentary deposits. This layer of iridium-enriched sediments has been found in many locations on different continents. After thoroughly studying this layer, scientists have generally concluded that it represents the signature of:
- one or more major meteorite impacts on Earth that disrupted food chains and caused the extinction of many species.
- extensive volcanism, including the eruption of flood basalts, that changed the composition of the atmosphere.
- a series of abnormally large coronal mass ejections from the sun that wiped out many plants and the species that fed on them.
- a period in which Earth's magnetic field decayed, increasing Earth's exposure to charged particles from space.
Answer to question 35
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: A. (Objective 0007) The anomalous levels of iridium in layers of sediments at the boundary between the Cretaceous and Tertiary periods have been shown to have been produced by the impact of one or more meteorites on Earth's surface approximately 65 million years ago. Although biodiversity was already decreasing toward the end of the Cretaceous period, a mass extinction event marks the boundary between these two periods. Since the initial discovery of the iridium-enriched sedimentary layers, scientists have discovered a large meteor crater that is coeval with the iridium-enriched sedimentary layers. It is believed that this meteor impact, and possibly other meteor impacts associated with it, were responsible for altering the climate and atmospheric conditions so much that many land-based food chains collapsed, leading to the extinction of many species, including most of the dinosaurs living at that time. There is evidence that other global changes that were occurring at that time may have contributed to the mass extinction. These include significant changes in sea level and extensive volcanism, including the eruption of the Deccan Trappes flood basalts that began approximately 68 million years ago.
Correct Response: A. (Objective 0007) The anomalous levels of iridium in layers of sediments at the boundary between the Cretaceous and Tertiary periods have been shown to have been produced by the impact of one or more meteorites on Earth's surface approximately 65 million years ago. Although biodiversity was already decreasing toward the end of the Cretaceous period, a mass extinction event marks the boundary between these two periods. Since the initial discovery of the iridium-enriched sedimentary layers, scientists have discovered a large meteor crater that is coeval with the iridium-enriched sedimentary layers. It is believed that this meteor impact, and possibly other meteor impacts associated with it, were responsible for altering the climate and atmospheric conditions so much that many land-based food chains collapsed, leading to the extinction of many species, including most of the dinosaurs living at that time. There is evidence that other global changes that were occurring at that time may have contributed to the mass extinction. These include significant changes in sea level and extensive volcanism, including the eruption of the Deccan Trappes flood basalts that began approximately 68 million years ago.
Question 36
36. Wave-cut platforms are fairly common features of the coast of California, Oregon, and Washington. These level areas that appear to have been eroded by wave action are often many feet above sea level. The current position of these geologic features results from:
- changes in sea level since the last continental glaciation.
- major storm events that occur over thousands of years.
- coastal uplift caused by the subduction of a tectonic plate.
- structural collapse of cliffs due to undercutting from wave erosion.
Answer to question 36
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: C. (Objective 0007) Wave-cut platforms are geologic features that are shaped at sea level by wave action on bedrock. Since the erosive power of the surf exists approximately at sea level and not much below sea level, these platforms are roughly horizontal. Once they have been eroded by wave action, tectonic forces can lift the wave-cut platforms above sea level. In many parts of the world, such as the west coast of North America north of Mendocino, California, this uplift is ongoing as the Juan de Fuca tectonic plate is subducted beneath the North American continental plate, forcing the overlying continental plate upward. Coastal California south of Mendocino is no longer actively being forced upward due to subduction; however, the extensive wave-cut platforms in California attest to repeated uplift due to tectonic forces that have occurred in the geologic past.
Correct Response: C. (Objective 0007) Wave-cut platforms are geologic features that are shaped at sea level by wave action on bedrock. Since the erosive power of the surf exists approximately at sea level and not much below sea level, these platforms are roughly horizontal. Once they have been eroded by wave action, tectonic forces can lift the wave-cut platforms above sea level. In many parts of the world, such as the west coast of North America north of Mendocino, California, this uplift is ongoing as the Juan de Fuca tectonic plate is subducted beneath the North American continental plate, forcing the overlying continental plate upward. Coastal California south of Mendocino is no longer actively being forced upward due to subduction; however, the extensive wave-cut platforms in California attest to repeated uplift due to tectonic forces that have occurred in the geologic past.
Question 37
37. The fossilization of ancient trees that produces petrified wood involves which of the following processes?
- The carbon in cellulose reacts with soil minerals to form calcium carbonate.
- Dissolved silica in groundwater precipitates within buried wood.
- The clay particles in mud fill cavities and pores in water-logged wood.
- Fine sediments encase buried logs producing detailed impressions.
Answer to question 37
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: B. (Objective 0007) Petrifaction of wood typically involves the movement of groundwater containing dissolved silica into wood. The petrified trees of the western United States typically were buried beneath or within deposits of volcanic ash. As groundwater moves through the ash, the water dissolves silica in the volcanic ash. It is the dissolved silica that then precipitates or crystallizes within the buried wood to form petrified wood. This process can be so complete that cells and other detailed structures within the wood are completely replaced with the silica, producing a mineralized replica of the original buried wood.
Correct Response: B. (Objective 0007) Petrifaction of wood typically involves the movement of groundwater containing dissolved silica into wood. The petrified trees of the western United States typically were buried beneath or within deposits of volcanic ash. As groundwater moves through the ash, the water dissolves silica in the volcanic ash. It is the dissolved silica that then precipitates or crystallizes within the buried wood to form petrified wood. This process can be so complete that cells and other detailed structures within the wood are completely replaced with the silica, producing a mineralized replica of the original buried wood.
Question 38
38. A paleontologist uncovers the fossilized bones of an early hominid that are estimated to be between one and two million years old. Given this estimated time range, which of the following is a dating technique that could be used to establish the age of the fossil?
- uranium-series dating of iron found in sediments surrounding the fossilized bones
- radiocarbon dating of wood or charcoal found adjacent to the fossilized bones
- potassium-argon dating of lava flows located above and below the fossilized bones
- fission-track dating of an interior section of the fossilized bones
Answer to question 38
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: C. (Objective 0007) Potassium-argon dating is based on measuring the radioactive decay product of an isotope of potassium (potassium-40) into argon. This method works on lava flows as they commonly contain potassium and can effectively bracket the age of a fossil by dating lava flows above and below the fossil being investigated. This technique has been widely used in Olduvai Gorge to date hominid fossil beds that are found between lava flows. Although the half-life of potassium-40 is 1.4 billion years, sophisticated analytical techniques can measure the ratio of daughter product (argon-40) to potassium-40 in rocks that have formed as recently as 100,000 years ago. Since potassium-40 has a 1.4 billion-year half-life, it is also effective for dating rocks from early in Earth's history.
Correct Response: C. (Objective 0007) Potassium-argon dating is based on measuring the radioactive decay product of an isotope of potassium (potassium-40) into argon. This method works on lava flows as they commonly contain potassium and can effectively bracket the age of a fossil by dating lava flows above and below the fossil being investigated. This technique has been widely used in Olduvai Gorge to date hominid fossil beds that are found between lava flows. Although the half-life of potassium-40 is 1.4 billion years, sophisticated analytical techniques can measure the ratio of daughter product (argon-40) to potassium-40 in rocks that have formed as recently as 100,000 years ago. Since potassium-40 has a 1.4 billion-year half-life, it is also effective for dating rocks from early in Earth's history.
Question 39
39. A continental landform characterized by low elevation, parallel ridges, and volcanic activity widens at a rate of about 7 millimeters per year. Which of the following geological processes is the dominant force driving this landform?
- divergence of continental crust along a rift
- subduction of oceanic crust beneath continental crust
- convergence involving the thrusting and folding of continental crust
- motion of continental crust in opposite directions parallel to a fault line
Answer to question 39
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: A. (Objective 0007) Rift valleys form where Earth's crust moves in opposite directions away from a rift, often forming the beginning of two new tectonic plates. This event results from the divergence, rather than convergence, of tectonic plates. The East African Rift, for example, widens at a rate of about 7 millimeters per year. Low elevation, parallel ridges, and volcanic activity also characterize rift valleys.
Correct Response: A. (Objective 0007) Rift valleys form where Earth's crust moves in opposite directions away from a rift, often forming the beginning of two new tectonic plates. This event results from the divergence, rather than convergence, of tectonic plates. The East African Rift, for example, widens at a rate of about 7 millimeters per year. Low elevation, parallel ridges, and volcanic activity also characterize rift valleys.
Question 40
40. Stromatolites are the earliest fossils formed by living organisms. Which of the following processes best describes how stromatolites form?
- Extremophilic microbes grow in high temperature environments, forming distinctive patterns in rock.
- Biofilms of microbes trap sediment in mats, forming a distinctive layered rock.
- Calcium carbonate shells of microbes merge over time, forming distinctive nodules within rock.
- Anaerobic microbes respire minerals, forming distinctive bands in subterranean rock.
Answer to question 40
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: B. (Objective 0007) Stromatolites are ancient trace fossils produced by bacteria, for example, cyanobacteria. The bacteria release secretions that make sediments in the environment, such as sand particles, which adhere to each other, forming long mats. The mats are laid down layer by layer, such that the oldest sediments are on the bottom and the youngest are on the top. The layers form distinctive rock-like structures that can take various shapes, such as domes.
Correct Response: B. (Objective 0007) Stromatolites are ancient trace fossils produced by bacteria, for example, cyanobacteria. The bacteria release secretions that make sediments in the environment, such as sand particles, which adhere to each other, forming long mats. The mats are laid down layer by layer, such that the oldest sediments are on the bottom and the youngest are on the top. The layers form distinctive rock-like structures that can take various shapes, such as domes.